Late Fees and Interest on GST
- 20 Sep 24
- 15 mins

Late Fees and Interest on GST
- What is Late Fees for GSTR 3B?
- Maximum Late Fee for GSTR 3B
- Due Date for GSTR-3B
- Waiver of late fee for GSTR 3B
- Form GSTR-3B Return
- Consequences of Not Paying a Late Fee of GST
- The Impact of Late Payments on Input Tax Credit Claims
- Understanding Fee Reductions and Waivers for GST Returns
- How Late Fee Notifications Enhance GST Return Filing Compliance
- How to Pay Late Fees in GST Portal?
- How to Calculate Interest Under GST?
Key Takeaway
- Timely filing of GSTR-3B is essential to avoid late fees and interest charges.
- The maximum late fee for GSTR-3B is capped at ₹5,000 per return, with lower caps for nil returns.
- Regularly check GST portal updates and notifications for potential late fee waivers.
- Non-payment of late fees can block future return filings and lead to additional penalties.
- Accurate record-keeping and timely reconciliation are crucial for managing GST liabilities and compliance.
What is Late Fees for GSTR 3B?
Late fees for GSTR-3B are imposed when a registered taxpayer fails to file their GST return by the due date. GSTR-3B is a monthly self-declaration that includes details of outward supplies, input tax credit, and tax liabilities. The late fee is charged for every day the return is delayed beyond the due date.
The government has set specific late fees for both central GST (CGST) and state GST (SGST). As per the current regulations, a late fee of ₹50 per day (₹25 each for CGST and SGST) is levied if there is tax liability. However, if there is no tax liability, the late fee is reduced to ₹20 per day (₹10 each for CGST and SGST).
| Tax Liability | Total Late Fee per Day | CGST Late Fee per Day | SGST Late Fee per Day |
|---|---|---|---|
| With Tax Liability | ₹50 | ₹25 | ₹25 |
| Without Tax Liability | ₹20 | ₹10 | ₹10 |
For those looking to avoid these penalties, timely filing is essential. In some cases, taxpayers may be eligible for a late fee waiver for GSTR-3B, which the government announces through notifications. It is important to stay updated with these notifications to take advantage of any waivers that may apply. Additionally, understanding the late fee structure can help businesses budget for potential delays and plan their tax payments more effectively.
Late fees not only increase the financial burden but can also lead to compliance issues. Regularly checking the due dates and ensuring that the GSTR-3B return is filed on time can prevent the accumulation of late fees and keep the business in good standing with tax authorities. The GST Council occasionally reviews these late fees, and any changes or updates should be closely monitored.
Maximum Late Fee for GSTR 3B

The maximum late fee for GSTR-3B has been capped to provide relief to taxpayers and avoid excessively high penalties. For normal taxpayers, the maximum late fee is ₹5,000 for each return filed late. This means that even if the delay extends over a long period, the total late fee payable will not exceed ₹5,000 per return.
For nil returns, where the taxpayer has no outward supplies or tax liabilities to declare, the maximum late fee is significantly lower. The government has capped the late fee for nil returns at ₹500 per return (₹250 each for CGST and SGST). This cap aims to reduce the burden on businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises (SMEs), encouraging compliance without imposing harsh financial penalties.
Understanding these caps is essential for businesses to manage their compliance costs effectively. Moreover, staying informed about any changes to these limits is crucial, as the government may revise them based on economic conditions and policy decisions.
Businesses should also note that while the maximum late fee provides a cap, it is still important to avoid delays. Accumulating multiple late returns can lead to significant total penalties even with the cap in place. Regular monitoring of filing deadlines and proactive tax management can help businesses avoid these costs. Late filing can also disrupt cash flow and overall business operations.
Due Date for GSTR-3B
The due date for filing GSTR-3B is typically the 20th of the following month for which the return is being filed. For instance, the return for January must be filed by the 20th of February. However, this date can be subject to change based on government notifications and extensions provided due to various reasons, such as technical issues with the GST portal or broader economic considerations.
Timely filing of GSTR-3B is critical to avoid late fees and interest charges. Businesses should mark their calendars and set reminders to ensure they meet these deadlines consistently. Additionally, the GST portal provides updates and notifications regarding due dates, which can help taxpayers stay informed.
💡If you want to pay your GST with Credit Card, then download Pice Business Payment App. Pice is the one stop app for all paying all your business expenses.
In some cases, the government may announce extensions to the due date, providing additional time for filing without incurring late fees. Taxpayers should keep an eye on official notifications and announcements to take advantage of any such extensions. Being proactive and organized can save businesses from unnecessary penalties and interest costs.
To ensure compliance, businesses should also consider the impact of filing late on their overall tax strategy, including potential interest charges and disruptions in cash flow. Regularly reviewing internal processes and ensuring that all necessary documentation is in place can help streamline the filing process and reduce the risk of missing deadlines. Keeping track of E-way Bills and other related documents is also crucial for smooth operations.
Waiver of late fee for GSTR 3B

A waiver of the late fee can provide significant relief to taxpayers who miss the due date for filing their GSTR-3B returns. The government occasionally announces waivers for late fees to reduce the financial burden on businesses, especially during challenging times such as economic downturns or pandemics.
These waivers are usually communicated through official notifications and have specific conditions and timeframes. For instance, the waiver might be applicable for returns filed within a certain period after the original due date. Businesses should stay updated with these notifications to ensure they can benefit from any applicable waivers.
To avail of a late fee waiver, taxpayers must file their returns within the specified period mentioned in the waiver notification. Failure to do so may result in the full late fee being applicable. It is also essential to understand that waivers typically apply to the late fee and not to the interest on delayed payments, which must still be paid as per the applicable rates.
Businesses should closely monitor the GST Council's announcements for any updates on late fee waivers. Properly managing the backlog of returns and ensuring compliance with all filing requirements can help avoid additional financial strain.
Form GSTR-3B Return
Form GSTR-3B is a simplified summary return that taxpayers need to file every month. It includes details of outward supplies, input tax credit claimed, tax payable, and tax paid. This form is crucial for the monthly payment of GST and helps the government in tracking the compliance of taxpayers.
The form requires taxpayers to provide consolidated details rather than invoice-wise information, making it simpler and quicker to file. However, accuracy is paramount, as errors can lead to penalties and interest. The GSTR-3B form must be filed even if there are no transactions during the month, in which case a nil return must be submitted.
Businesses must ensure that all details in the GSTR-3B form match the records in their accounting systems. Discrepancies can lead to issues during audits and may attract penalties. Regular reconciliation of records and timely filing of returns can help avoid these problems.
Form GSTR-3B should be filed considering the annual turnover slab of the business, ensuring all outward supplies and taxable supplies are correctly reported. Understanding the nuances of normal return and composition levy can aid in accurate return filing.
Consequences of Not Paying a Late Fee of GST
Failing to pay the late fee for GST can lead to several consequences, including the inability to file subsequent returns. The GST portal blocks the filing of future returns until the outstanding late fees are paid. This can cause a ripple effect, leading to further non-compliance and additional penalties. Such delays can also impact the overall financial health of the business by causing cash flow disruptions.
Non-payment of late fees also attracts interest on the outstanding amount, increasing the financial burden on the taxpayer. The interest is calculated based on the outstanding tax amount and the number of days the payment is delayed, typically at a rate of 18% per annum. This additional cost can quickly accumulate, especially for businesses with significant tax liabilities.

Moreover, persistent non-compliance can result in the issuance of notices by the GST authorities, leading to audits and potential legal action. These legal complications can further strain the resources of the business, both financially and operationally. In severe cases, non-compliance can lead to the suspension or cancellation of GST registration, severely impacting the ability to conduct business.
To avoid these issues, businesses must prioritize timely payment of late fees. Regularly checking the GST portal for any outstanding dues and promptly addressing them can prevent complications and ensure smooth compliance. Establishing a robust internal process for tracking GST filings and payments can help mitigate the risk of non-compliance.
Businesses should also consider the aggregate turnover and annual aggregate turnover when planning their GST compliance strategy. Regularly updating the GST return filing status and ensuring all return statements are accurate can prevent future issues.
The Impact of Late Payments on Input Tax Credit Claims
Late payment of GST can significantly affect the ability of registered persons to claim input tax credit (ITC). If a taxpayer fails to file their return within the specified tax period, the delay can result in disqualification from claiming excess input tax credit for that period. The number of days of delay directly impacts the eligibility for ITC claims. For instance, if the return for the previous month is filed late, the ITC for that month may be denied, which can disrupt the business's capital relief and cash flow management.
Late payments also lead to monetary penalties and interest charges, adding to the financial burden of the business. The maximum limit on late fees is designed to cap these penalties, but even within these limits, the costs can accumulate quickly. Additionally, non-compliance with return filing dates, especially for monthly returns and quarter returns, can lead to further complications in managing tax liabilities.
Understanding the implications of late payments on ITC claims is crucial for businesses. It emphasizes the importance of timely filing and adherence to return mandates to avoid penalties and ensure the smooth operation of financial processes. Regular monitoring of return filing dates and prompt action to file returns can help businesses maintain their ITC claims and overall financial health.
Understanding Fee Reductions and Waivers for GST Returns
Fee reductions and waivers offered by the government can provide significant relief to taxpayers who miss GST return filing deadlines. These provisions aim to reduce the financial burden on registered persons by capping the maximum late fee and offering partial waivers under specific conditions. Late fee notifications, issued periodically, inform taxpayers about the availability of these waivers and the criteria for eligibility.
For instance, a fee reduction/waiver might be applicable if returns are filed within a specified period following the due date. Such waivers can apply to various transactions, including intrastate supplies, offering broader relief to businesses. Understanding the conditions and timelines for these waivers is essential for businesses to benefit from them effectively.
Moreover, compliance with return mandates is critical to qualify for these waivers. Businesses must ensure timely filing of returns, both monthly and quarterly, to avoid incurring late fees. Staying informed about the latest notifications from the GST Council and tax authorities helps businesses take advantage of available waivers, manage their tax liabilities more efficiently, and avoid unnecessary penalties.
How Late Fee Notifications Enhance GST Return Filing Compliance
Late fee notifications play a vital role in encouraging GST return filing compliance among taxpayers. These notifications provide crucial information about the penalties for delayed filings, including monetary penalties and restrictions on input tax credit claims. By clearly outlining the consequences of non-compliance, these notifications incentivize timely filing.
Understanding the details within these notifications, such as the maximum limit on late fees and the number of days of delay that will incur charges, helps businesses plan their return filing dates more effectively. Notifications also highlight any fee reductions or waivers available, offering financial relief for those who miss deadlines. For instance, partial waivers might be granted if returns are filed within a certain period after the due date.
Staying updated with late fee notifications ensures that businesses can avoid unnecessary penalties and maintain smooth financial operations. Compliance with return mandates, including monthly and quarterly returns, is essential for avoiding disruptions in business processes. By adhering to these notifications, businesses can manage their tax obligations efficiently, ensuring that the payment of Rs. is completed on time and maintaining overall document compliance.
How to Pay Late Fees in GST Portal?
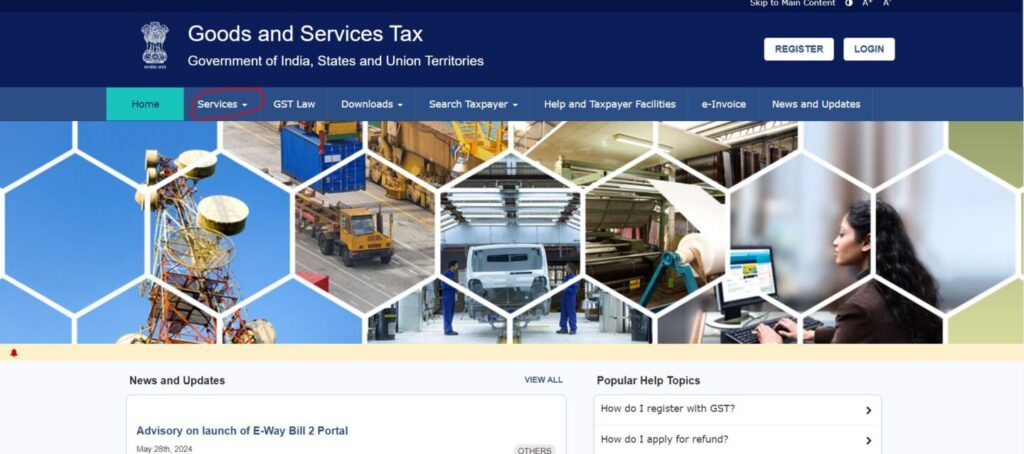
Paying late fees on the GST portal is a straightforward process. Taxpayers need to log in to the GST portal, navigate to the "Services" section, and select "Returns." Under the "Returns" section, they should choose the relevant return period for which the late fee is applicable.
Once the return is selected, the portal will display the amount of late fee due. Taxpayers can then proceed to make the payment using various online payment options available on the portal, such as net banking, credit/debit cards, or via a challan at designated banks.
After the payment is completed, the system will generate a payment receipt, and the late fee will be adjusted against the respective return. It is essential to ensure that the payment details are correctly recorded and that the receipt is saved for future reference.
Ensuring timely GST payment and avoiding delay in filing can help businesses maintain good standing with tax authorities and avoid additional penalties.
How to Calculate Interest Under GST?
Calculating interest under GST involves determining the amount payable for delayed payment of tax. The interest rate for delayed payment is typically 18% per annum, calculated from the day following the due date until the actual payment date. For example, if the due date for payment was the 20th of a month and the payment was made on the 30th, interest is calculated for ten days.
To calculate the interest, determine the outstanding tax amount and the number of days the payment is delayed.
Use the formula: (Outstanding Tax Amount) x (Interest Rate) x (Number of Days) / 365.
This will give the interest payable.
It is crucial for businesses to regularly monitor their GST liabilities and ensure timely payments to avoid incurring interest. Accurate record-keeping and timely reconciliation of accounts can help manage this effectively and ensure compliance with GST regulations.
Keeping track of quarterly returns, annual returns, and other business compliances can help in managing the interest calculations efficiently. Businesses should also consider the impact of delay for turnover and plan their cash flow accordingly to avoid disruptions.
Understanding the filing return process and maintaining a schedule for all return filers can help in reducing the instances of late filing and associated penalties. Ensuring that the return statement and payment of GST liability are accurate and timely can enhance overall business compliance.
 By
By